Token
Whenever we are discussing a Java program, it basically deals with the characters (i.e., an alphabet/ a number/ special characters). Each individual character used in the Java program is termed a Token.
Token is the fundamental unit of a Java program.
It may be compared with the cell in the human body. (As a cell is the fundamental and functional unit of the human body, a token may also be referred to as a cell of the Java program).
There are various types of tokens that are available in Java. They are :
Keywords
- Identifiers
- Operators
- Literals
- Separators
In Simple words -> What you type is what you get.
Integer Literals - whole numbers having positive or negative values. e.g.: 104, 550, -35, etc.
Real Literals - represent numbers with decimal points. e.g.: 26.54, 0.54, -7.658, etc.
Character Literals - All alphabets, digits, and special characters can be termed character literals. e.g.: 'A', 'd', '4', '*'.
String Literals - It consists of a group of characters inside double quotes. e.g.: "Year2022", "HackForCode", etc.
Boolean Literals - It consists of the keywords; true and false. These keywords can be used anywhere you need a test.
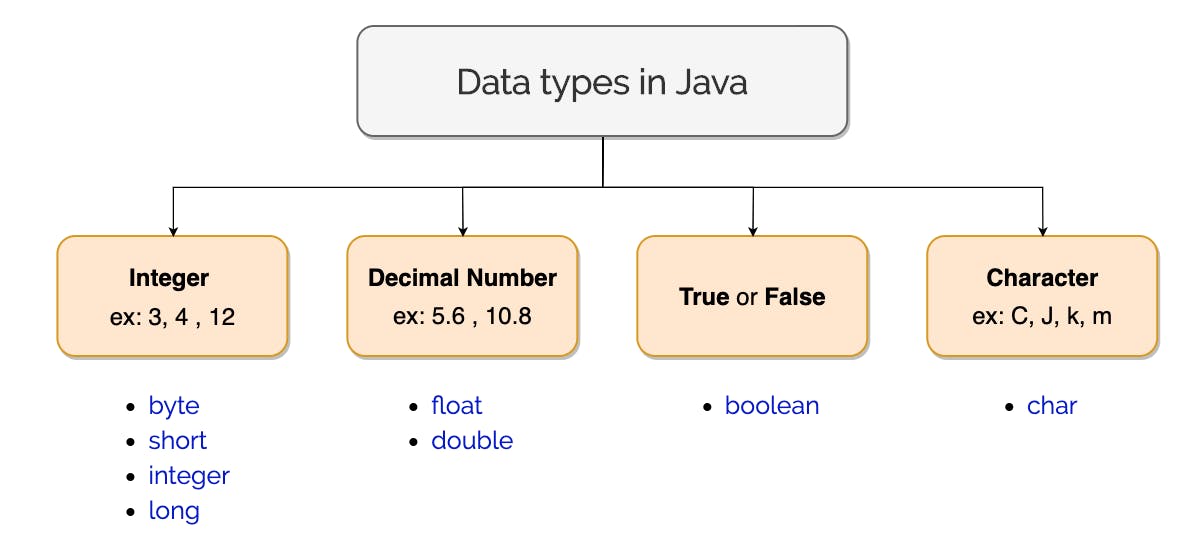
Data Types
In Java, we have to deal with various types of data, hence it becomes necessary for a programmer to select an appropriate data type according to the data taken in a program.
Primitive Data Types
- Primitive data types are built-in data types.
- Primitive data types are those data types that are not breakable.
- Java supports 8 types of primitive data types.
Non Primitive Data Types
- They are basically defined as derived data types.
- They are directly or indirectly dependent on primitive data types.
They are also called the Reference data type.
Array
- String
- Class
- Interface
Integar Type
- A variable declared integer type contains a whole number.
- They may be a positive or a negative number but without a decimal point.
| Type | Size | Use |
| byte | 1 byte | applied for a very small value range from -128 to 127 |
| short | 2 bytes | applied for a small range of value varies between -32768 to 32767 |
| int | 4 bytes | applied for integers that are more than short integers |
| long | 8 bytes | applied for large integers |
Note:- 1 byte = 8 bits
Float Types
| Type | Size | Use | Precision |
| float | 4 bytes | It represents a fractional number with a small ranges | 7 digits |
| double | 8 bytes | It represents a fractional number with wide range values | 15 digits |
- some valid floating points:
- 5.0
- +3.4256, .58
some invalid floating points:
1000 (Decimal missing)
- (fractional portion is missing)
- ±20.123 (Both signs are not allowed)
- 20,23.154 (comma not allowed)
- 20 23.154 (blank space between digits not allowed & blank space after sign not allowed)
Representation in Exponent form in Java
9.136 x 10^8 can be written as 9.136E8
- 9.136 x 10^-8 can be written as 9.136E-8
Character Types
- It contains a single character.
- There are 256 characters available with the computer. These characters are termed as ASCII characters.
- Each ASCII character is allotted a specific numeric code called ASCII code.
- The ASCII codes of the characters range from 0 to 255.
ASCII code of the characters is as follows :
- A - Z : 65 - 90
- a - z : 97 - 122
- 0 - 9 : 48 - 57
The character types in Java are as follows :
| Type | Size | Example |
| char | 2 bytes | 'A', 'd', '4' |
| string | more than 2 bytes | "Ad4", "H" |
Note:
- A character is enclosed in single quotes (' ')
Strings are enclosed in double quotes (" ")
Boolean Type
It contains a constant as True or False.
Variables
A variable is the name of the location where the value is stored.
- This location exists in computer memory where the value can be stored and in case of need, it can be retrieved.
Declaration
- int val;
- float points;
Assignation
- val = 12;
- points = 52.314f
Initialization
M-1: Initialize a variable in two statements
dataType variableName;
variableName = value;
M-2: Initialize in one statement
dataType variableName = value;
Identifiers
- All java components require names. Names of variables, methods, classes, packages, etc. is known as identifiers.
- It allows a programmer to refer to the item from other places in the program.
Rules for naming a variable
- A variable may have any number of characters.
- It may contain alphabets, digits, and underscore.
- Variable name should be meaningful and easily depict the logic.
Rules for variable to be invalid
- Variable names should not start with a digit or special character. (It can start with an underscore)
- A variable name should not include a space in between its characters.
- A digit should not be applied in between the characters of a variable name.
- A variable name should not be a Keyword.
keyword
Java Reserved words are those keywords that cannot be used as variable names in the programs. A list of java reserved keywords has been given below:
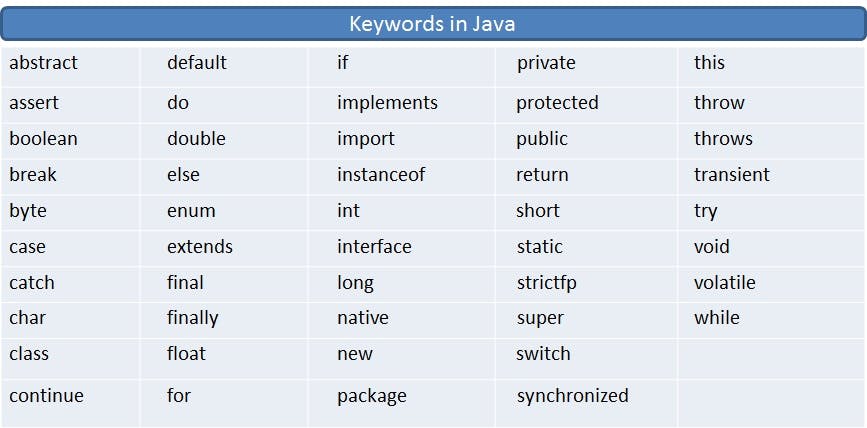
true, false, and null are not reserved words but cannot be used as identifiers.(because they are literals of built-in types).
Punctuators
- Punctuators are the signs used as special characters in Java.
- some of them are . (dot), ; (semi colon), etc.
- Dot (.) is used to represent the scope of a function.
- Semi Colon (;) is used in the java programs as a statement terminator. Any line continued after a semi-colon is treated as the next line.
Separators
They are the special characters in Java, which are used to separate the variables or the characters. Example :- Comma (,) , Brace ( ) , Culry Braces { } , Square Braces [ ] , etc.
Operators
In the next lecture. Till then keep learning!
Keep Growing!!

